Understanding Prefabricated Homes: Affordable and Efficient Housing Options
Prefabricated homes are residential units manufactured in controlled facilities and assembled on-site. This approach integrates standardized components, quality control, and streamlined logistics to reduce on-site labor and construction time. The article explains how prefab housing functions and key considerations.
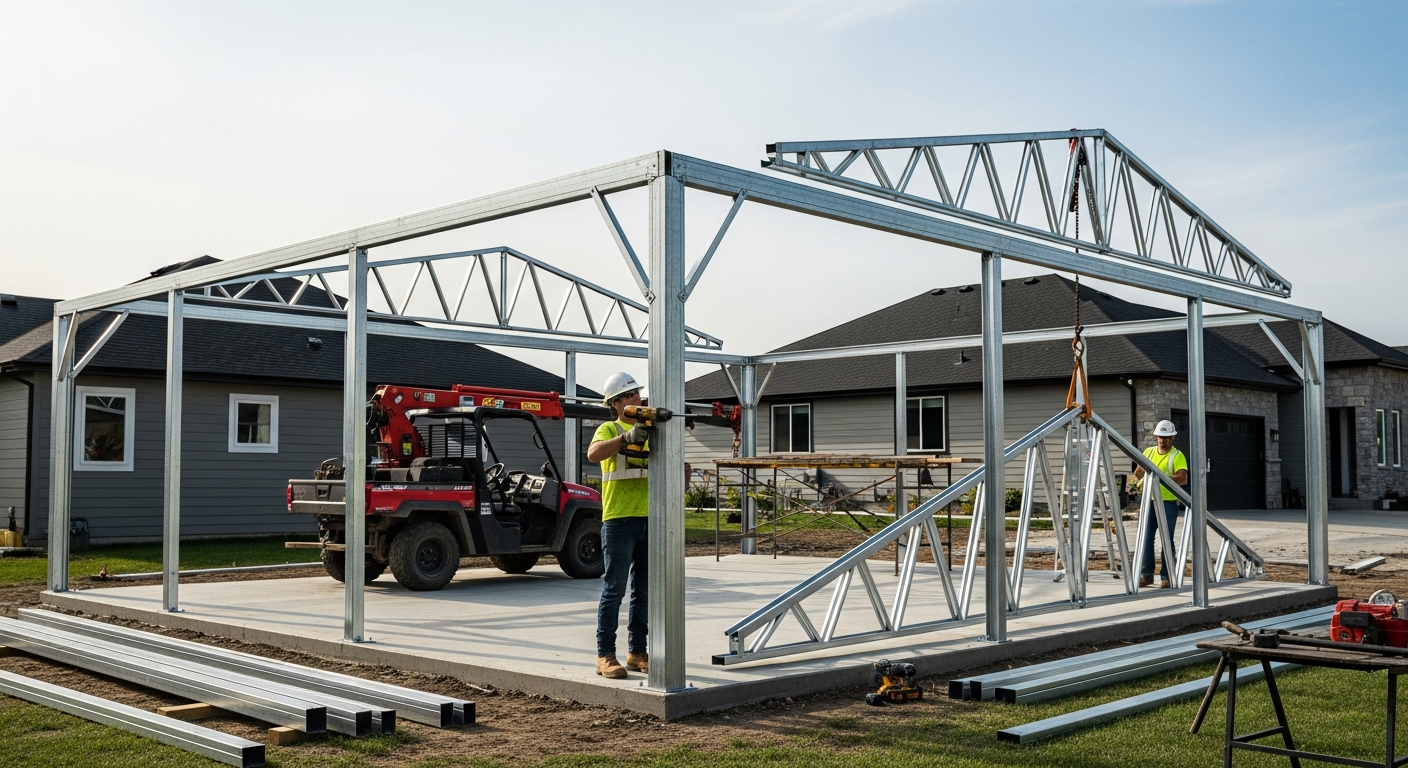

Prefabricated homes have emerged as a compelling alternative to conventional construction, combining modern manufacturing techniques with residential design to create efficient housing solutions. As housing costs continue to rise across the United States, more Americans are exploring prefab options as a pathway to homeownership that doesn’t compromise on quality or customization.
What are prefabricated homes and how do they work?
Prefabricated homes are residential structures manufactured in factory settings using standardized construction processes. The term encompasses various types including modular homes, manufactured homes, and panelized construction systems. Unlike traditional site-built homes, prefab structures are constructed in climate-controlled facilities where materials remain protected from weather delays and quality control measures can be consistently applied.
The manufacturing process typically involves creating sections or modules that are later transported to the building site for final assembly. This approach allows for simultaneous site preparation and home construction, significantly reducing overall build times from months to weeks in many cases.
How do efficient prefabricated homes compare to traditional construction?
Prefabricated construction offers several advantages over traditional building methods, particularly in terms of efficiency and waste reduction. Factory-built homes generate approximately 50% less waste than site-built construction due to precise material calculations and controlled manufacturing environments. The assembly-line approach also enables better quality control, as each component undergoes inspection before leaving the facility.
Energy efficiency often surpasses traditional construction standards, as prefab manufacturers can implement consistent insulation techniques and air sealing methods that might be challenging to achieve on-site. Many prefab homes exceed local energy codes and can incorporate advanced building technologies more easily than traditional construction.
What types of prefabricated home designs are available?
Modern prefabricated homes span a wide range of architectural styles and sizes, from compact single-family units to expansive multi-story residences. Modular homes offer the most customization options, allowing buyers to select floor plans, finishes, and architectural details similar to traditional construction. These homes are built in sections that connect on-site to create seamless living spaces.
Manufactured homes, built to HUD standards, provide affordable entry-level options with standardized designs that prioritize cost-effectiveness. Panelized systems offer a middle ground, where wall panels, roof trusses, and floor systems are factory-built but assembled using traditional construction techniques on-site.
Understanding prefabricated home costs and providers
Prefabricated home costs vary significantly based on size, design complexity, and regional factors, but generally offer savings compared to traditional construction. The controlled manufacturing environment and reduced labor costs contribute to these potential savings.
| Home Type | Provider | Cost Estimation |
|---|---|---|
| Modular Homes | Champion Homes | $80-$120 per sq ft |
| Manufactured Homes | Clayton Homes | $45-$75 per sq ft |
| Panelized Systems | Lindal Cedar Homes | $100-$150 per sq ft |
| Kit Homes | Unity Homes | $120-$180 per sq ft |
| Luxury Modular | Method Homes | $200-$300 per sq ft |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
These estimates typically include the basic structure but may not cover site preparation, foundation work, utility connections, or local permitting fees, which can add $20,000 to $50,000 to the total project cost depending on location and site conditions.
How do zoning laws and building codes affect prefab installation and global uses?
Zoning regulations and building codes significantly impact prefabricated home installation, with requirements varying by municipality and state. Many jurisdictions now treat modular homes identically to site-built construction once they meet local building codes, but manufactured homes may face restrictions in certain residential zones.
Building code compliance is typically addressed during the manufacturing process, with homes designed to meet or exceed the International Residential Code (IRC) standards used in most U.S. markets. However, local amendments and specific regional requirements may necessitate design modifications or additional inspections during installation.
Permitting processes for prefab homes generally follow similar timelines to traditional construction, though some municipalities have streamlined approval processes for factory-built homes that arrive with pre-approved structural certifications.
Prefabricated construction continues to evolve as building technologies advance and housing affordability challenges persist across the United States. The combination of reduced construction time, consistent quality control, and potential cost savings makes prefab homes an increasingly viable option for first-time buyers, downsizing retirees, and anyone seeking efficient housing solutions. Understanding the various types, costs, and regulatory requirements helps potential homeowners make informed decisions about whether prefabricated construction aligns with their housing goals and local market conditions.